A
Accounts Payable (AP)
Money a business owes to suppliers or service providers for goods or services received on credit.
Accounts Receivable (AR)
Payments expected from clients or customers for products or services delivered.
Accounting Standards
Guidelines that ensure financial statements are accurate, consistent, and comparable across companies.
Audit
An independent review of financial records to ensure accuracy, transparency, and compliance with laws.
B
Balance Sheet
A financial statement showing a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
Bookkeeping
Recording daily financial transactions such as sales, expenses, and payments.
Budgeting
Planning and allocating resources to meet business goals efficiently.
C
CFO Services
Strategic financial leadership that helps businesses with planning, reporting, compliance, and growth strategies.
Cash Flow
The movement of money in and out of a business, indicating liquidity and financial health.
Compliance
Adhering to laws, tax regulations, and industry standards to avoid penalties.
Corporate Governance
Systems and processes ensuring accountability, fairness, and transparency in a company’s operations.
D
Depreciation
The reduction in value of an asset over time due to usage or wear and tear.
Dividends
Profits distributed to shareholders from a company’s earnings.
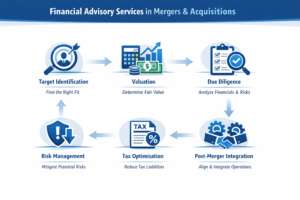
Due Diligence
A detailed investigation of a business’s finances and operations before a merger, acquisition, or investment.
E
EBITDA
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization; a measure of business profitability.
Equity
Ownership interest in a company, often represented by shares or retained earnings.
Expense Management
Controlling and monitoring expenses to improve profitability and efficiency.
F
Financial Forecasting
Predicting future revenues, expenses, and cash flows to support business decisions.
Financial Reporting
Preparing statements like balance sheets and profit & loss reports for stakeholders.
Fixed Assets
Long-term resources such as property, equipment, and machinery used in business operations.
G
GAAP
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles – standard rules for preparing financial statements.
Growth Strategy
A plan to increase a business’s revenue, market share, and profitability over time.
I
Income Statement
A financial report showing revenue, expenses, and net profit over a specific period.
Internal Controls
Processes designed to protect company assets, ensure accurate reporting, and prevent fraud.
Investment Advisory
Professional guidance on managing investments and building wealth.
L
Liabilities
Financial obligations or debts a company owes to third parties.
Liquidity
A measure of how easily assets can be converted into cash to meet obligations.
M
Management Reporting
Reports providing insights into business performance to help management make informed decisions.
Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)
Combining or acquiring companies to grow operations, market share, or capabilities.
O
Outsourced Accounting
Delegating finance and accounting tasks to external experts for efficiency and cost savings.
Overheads
Ongoing business expenses not directly tied to production, like rent or utilities.
P
Payroll Management
Managing employee salaries, taxes, and statutory compliance efficiently.
Profit & Loss Statement (P&L)
A report showing revenues, expenses, and net profit or loss over a given period.
Private Equity
Investment funds providing capital to private companies in exchange for ownership or control.
R
Return on Investment (ROI)
A measure of the profit or loss generated relative to the money invested.
Risk Management
Identifying and minimizing financial, operational, and strategic risks.
S
Scalability
A business’s ability to grow revenue without proportionally increasing costs.
Statutory Audit
A legally required audit to ensure compliance with regulatory and financial standards.
Strategic Advisory
Expert guidance to support long-term business planning and decision-making.
T
Tax Advisory
Professional services to optimize taxes legally, ensure compliance, and plan for savings.
Transfer Pricing
Setting prices for transactions between related companies to comply with tax laws.
Treasury Management
Managing company cash, investments, and financial risk to maintain liquidity.
V
Valuation
Determining the economic value of a business, asset, or investment.
Variable Costs
Costs that change with the level of business activity, such as raw materials or commissions.
W
Working Capital
The difference between current assets and current liabilities, showing a company’s short-term financial health.
Wealth Management
Comprehensive planning and investment management for individuals, families, or businesses.
FAQ Questions & Answers
1. What is Accounts Payable (AP)?
Accounts Payable refers to the money a business owes to vendors for goods or services purchased on credit.
2. What is Accounts Receivable (AR)?
Accounts Receivable is the amount customers owe a business for products or services already delivered.
3. Why is cash flow important for a business?
Cash flow shows how money moves in and out of a business and determines its ability to operate smoothly.
4. What does CFO services mean?
CFO services provide strategic financial leadership, including planning, reporting, compliance, and growth guidance.
5. What is a balance sheet used for?
A balance sheet shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
6. What is EBITDA in simple terms?
EBITDA measures a company’s profitability before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
7. What is working capital?
Working capital is the difference between current assets and current liabilities, showing short-term financial health.
8. What is financial compliance?
Financial compliance means following tax laws, accounting standards, and regulatory requirements to avoid penalties.
9. What is the purpose of a statutory audit?
A statutory audit ensures financial statements comply with legal and regulatory standards.
10. What is valuation in business finance?
Valuation determines the economic value of a company, asset, or investment.